 Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers among women in the United States. It is also one of the leading causes of mortality in all races. According to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention or CDC (as cited in: http://www.cdc.gov/cancer/breast/statistics/), in the year 2009, about 211,731 women in the United States were diagnosed with breast cancer while 40,676 women have died from it. And according to breastcancer.org, in 2011, an estimated 230,480 new cases of invasive breast cancer were expected to be diagnosed in women in the U.S., along with 57,650 new cases of non-invasive (in situ) breast cancer.
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers among women in the United States. It is also one of the leading causes of mortality in all races. According to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention or CDC (as cited in: http://www.cdc.gov/cancer/breast/statistics/), in the year 2009, about 211,731 women in the United States were diagnosed with breast cancer while 40,676 women have died from it. And according to breastcancer.org, in 2011, an estimated 230,480 new cases of invasive breast cancer were expected to be diagnosed in women in the U.S., along with 57,650 new cases of non-invasive (in situ) breast cancer.
Breast cancer is an uncontrolled growth of breast cells. It is also a type of cancer that forms tissues within the ducts that bring milk and to the glands that produce milk. It occurs to both men and women, although it is more common in women.
Risk factors include the following:
• Age- As you grow older, the greater chances of having breast cancer
• Family History – It has been proven that if you have a close relative (mother, sister) doubles your risk
• Early menarche and late menopause – Women who started their menstruation (those earlier than 12 years old) and those who went through their menopause (later than 55) have increased chances
• Obesity
• Alcoholism
• Nulligravid (no child) or those who had their first child on their 30’s
• Use of oral contraceptives for the last 10 years
Early detection and diagnosis must be done to be aware of your condition and to receive proper treatment and management. Breast self-examination after a week of your menstruation also helps in examining if there are lumps, lesions or any malformations on your breasts. However, if you’re over 40 and have a high risk of developing breast cancer as stated above, you must undergo some tests and physical examination.
Mammogram provides an x-ray picture of the breast. It is used to visualize the normal and abnormal structures within the breast. It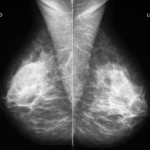 can be able to determine if cysts, calcifications and tumors present. A mammogram can either be a screening mammogram or a diagnostic mammogram. A screening mammogram is done even without signs and symptoms present, though it provides images to make it possible to detect tumors that cannot be felt. On the other side, a diagnostic mammogram is done to be able to determine and diagnose the extent and degree of the breast cancer.
can be able to determine if cysts, calcifications and tumors present. A mammogram can either be a screening mammogram or a diagnostic mammogram. A screening mammogram is done even without signs and symptoms present, though it provides images to make it possible to detect tumors that cannot be felt. On the other side, a diagnostic mammogram is done to be able to determine and diagnose the extent and degree of the breast cancer.
In mammogram, the patient’s breasts are placed between 2 firm and flat panels and plates. Then a firm but gentle compression is then applied on the breasts. The patient may feel a little discomfort but it will only last for a few seconds. The compression must be applied so as to fully visualize the inner structures of the breasts. Without the compression, the image will be blurry and will have a poor resolution. During the test, the patient may be asked to stand still and hold her breath. Mammogram provides structural imaging, which means it has the ability to locate the suspicious areas within the breast.
The result of the mammogram is usually within 30 days. Possible abnormal findings can include calcifications, masses or lumps, distorted tissues and some dense areas which only appear on one breast.
However, mammogram, the test itself has limitations and some risks. Since it is a form of x-ray procedure, it exposes the patient to radiation though it is only a low dose. Though radiation is not good for the health because it increases the risk for cancer, doctor’s advise is very much important. But usually it outweighs the benefits of the mammogram. Another limitation for mammogram is that it is only a part of the complete breast exam. It needs other tests to be able to determine the presence of abnormalities.
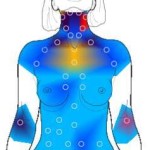 Another procedure used to detect abnormal structures of the breasts is the thermography. Thermography is a non-invasive and a safe procedure which uses digital infrared imaging to detect malformations and abnormal structures within the breast tissues. Unlike the mammogram which involves compression of the breasts, thermogram uses infrared sensors to actually detect increased vascularity and presence of heat. Thermography utilizes a principle that in pre-cancerous tissues and in the areas around a developing breast cancer has always increased metabolic activity and vascular circulation. And with that principle, it can be able to detect thermal signs which might detect the presence of a pre-cancerous state of the breast or if the breast is on the early stage, not enough to be detected by mammogram, physical examination or other imaging tests. Thermography uses functional imaging which means it is capable of detecting physiologic changes but it cannot locate the exact area of suspicion inside the breast.
Another procedure used to detect abnormal structures of the breasts is the thermography. Thermography is a non-invasive and a safe procedure which uses digital infrared imaging to detect malformations and abnormal structures within the breast tissues. Unlike the mammogram which involves compression of the breasts, thermogram uses infrared sensors to actually detect increased vascularity and presence of heat. Thermography utilizes a principle that in pre-cancerous tissues and in the areas around a developing breast cancer has always increased metabolic activity and vascular circulation. And with that principle, it can be able to detect thermal signs which might detect the presence of a pre-cancerous state of the breast or if the breast is on the early stage, not enough to be detected by mammogram, physical examination or other imaging tests. Thermography uses functional imaging which means it is capable of detecting physiologic changes but it cannot locate the exact area of suspicion inside the breast. 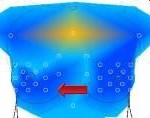
How thermogram is performed? The patient is placed on temperature-controlled room to allow the body to cool off from the external conditions. The patient is positioned on a thermal imaging camera wherein the technician will take digital pictures. The entire procedure usually lasts for 5-15 minutes. Then the images are then sent to a physician for an analysis of the amount of heat present and the symmetry of heat patterns. Heat patterns usually suggest presence of inflammation or infection.
Mammography and thermography are two procedures used to detect the presence of abnormality within the breasts. Each one cannot replace the other. Both tests are adjunctive in detecting abnormalities. A physiologic procedure like thermography cannot replace an anatomical procedure like mammography and vice versa. The two procedures if combined can determine the presence of defect but  the two cannot determine if the suspected tissue is cancerous or not, only the biopsy does.
the two cannot determine if the suspected tissue is cancerous or not, only the biopsy does.
With whichever procedure you may undergo or if the doctor advised you to take the two said procedures, always remember that, early detection is essential to know the necessary measures to be taken.
Johanna Oosterwijk N.D.